Patients today have greater power and knowledge thanks to the Internet and the modern information era. In turn, emerging technologies propose breakthroughs in both therapies and the overall healthcare value chain. What exactly is Patient Centric Care, and why will it bring in a new era of healthcare?
Medicine is a science that has been practiced for over 6,000 years. The various actors involved began with the same goal in mind: to learn about human biology and to develop cures for illnesses and diseases.
Although much has changed and evolved in six millennia, the truth is that the way patients and doctors interact with each other has stayed virtually unchanged.
However, in recent years, this typically top-down dynamic, in which doctors and the pharmaceutical industry were at the top and consumers were at the bottom, has begun to change toward models that place patients at the center of decision-making.
Technology and health: allies for patient empowerment
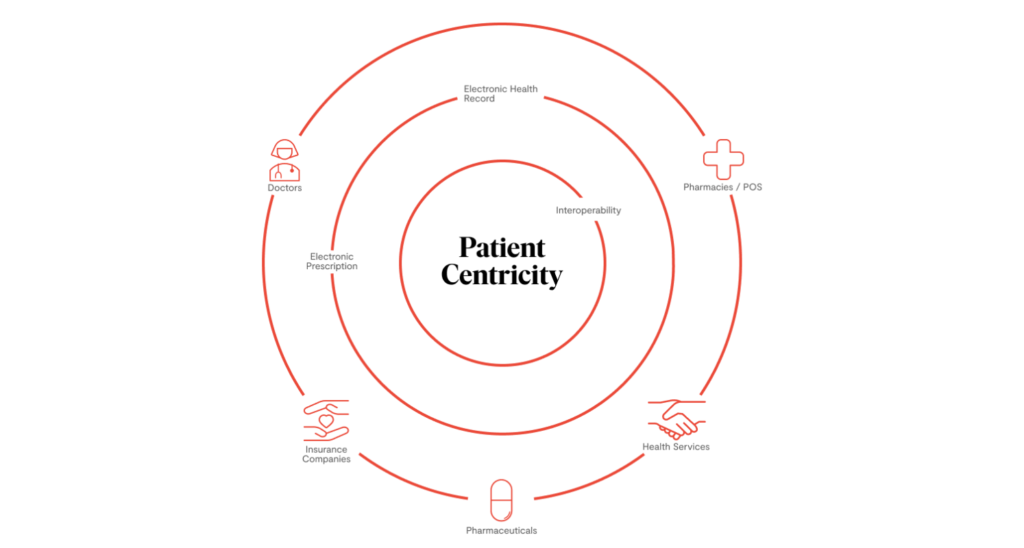
Health involves not only doctors and patients, but also laboratories and pharmacies, insurance firms, government, and even major and small technological companies.
According to a recent Statista report, MedTech (or “Medical Technology”) is a global sector worth more than USD 400 billion each year. The United States and China are leading the industry’s expansion, with nearly 40% of the world’s medical device market sales.
The new approach to medicine, which is undergoing a deep digital transformation, completely alters the treatment paradigm. Previously, doctors were the ones who made decisions concerning patients, but now patients are the ones who hold the most power..
In view of the facts, the entire ecosystem works to provide patients with both value and meaningful experiences.
These are some of the elements that influence this shift:
- Technology, which now allows us to have unified, consolidated clinical records, so that information is available to all clinicians.
- Humanization of treatment, since professionals, with their great knowledge, now communicate more clearly with patients.
- The chance to establish truthful information sites that provide significant information while also persuading patients to see an expert.
What are the advantages of becoming Patient-centric?
1. Health-care systems that are more user-friendly, with greater clinical outcomes. By developing systems to make the patients’ life easier, they will have a more fluid experience, increasing their odds of adhering to their therapy, follow-up, and control.
2. Empowerment of the patients, so that they have more control over the disease they are suffering from.
3. Personalized treatments, as opposed to the industry’s conventional prescription of more generic drugs and solutions. Specific medicines are now designed for each patient as a result of innovation.
4. More innovation, since the industry as a whole is being pushed, in a good way, to offer innovative solutions across its value chain, from manufacturing and distribution to marketing.
What are the challenges that lie ahead?
The key problem is cooperation among the ecosystem’s multiple stakeholders, which include laboratories, insurance companies, pharmacies, doctors, and public and private hospitals. Of course, everyone has their own interests and goals, but in the modern era of medicine, it is critical to develop a healthy work environment among all parties that prioritizes the patients and places them at the center of decision-making.
On the other hand, there are regulatory barriers that have been imposed for models that are gradually falling behind. These, for example, prevent any actor other than a doctor from knowing and using patient data, as well as speaking with them.
To ensure the proper development of medicine, regulations and frameworks must be modified to support work schemes in which information is transparent to all stakeholders, in order to create more efficient and tailored processes while always keeping data security and privacy in mind.
The third and last obstacle is educating patients, who, in most cases, relate to their body and health in a reactive manner, when the problem is already present, rather than taking preventive measures — such as regular check-ups or wearing gadgets that measure health factors.
According to Statista, the worldwide digital health market will be worth more than USD 500 billion by 2025. Currently, the health information technology sector of the market is predicted to provide the highest proportion of revenue, reaching around USD 280 billion by 2021.
It should be highlighted that the use of technology allows not only for the prediction of diseases and illnesses, which improves quality of life, but also for cost savings and data interoperability for the entire ecosystem.
How to tackle these problems?
- Promote collaboration between the parties.
Innovation hubs foster this form of collaboration environment by facilitating the gathering of various participants.
Also, in the manufacture and distribution of medications, a new breed of medical startups is gaining ground on established corporations. This has an influence on traditional laboratories, which are being compelled to cooperate more dynamically with the other actors in the sector, which is a good thing.
- Encourage innovation
The majority of health-care breakthroughs in recent years have come from entrepreneurs, bankers, developers, and technology businesses rather than doctors or laboratories.
The rise of more healthcare startups whose primary business is prevention requires that large corporations begin innovating.
There are currently Pharma startups, tiny laboratories, and insurance organizations that use cutting-edge technology, such as Artificial Intelligence. This causes a critical mass of change that drives the entire established industry to consider innovation.
We encourage you to contact Alex Ruiz, Multiplica’s Health Industry Global Head, who recently participated in the Barcelona Health Hub panel “Patient-centered omnichannel: Helping patients improve their adherence to treatment.”
Multiplica has extensive experience in the health industry, having worked with companies such as Gebro, Grifols, Almirall, Novartis, Lilly, and Amgen, among others.